Award-winning instructors
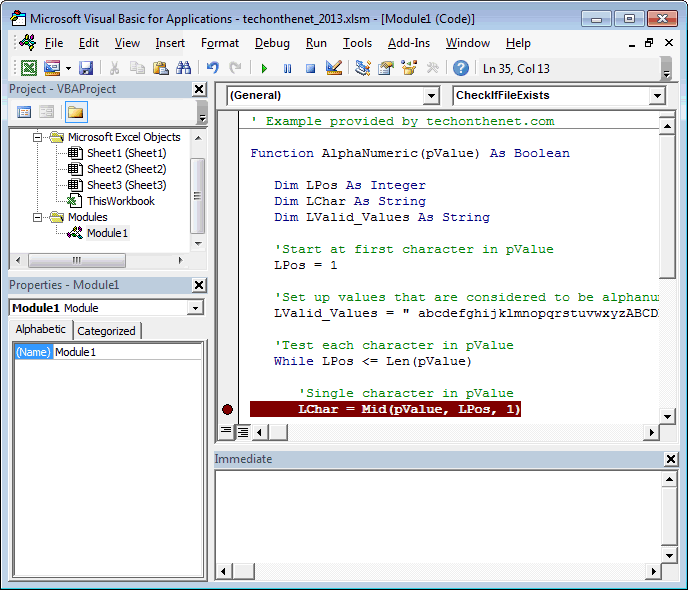
Microsoft just released a new build of Excel that contains a new VB Editor, which we use to write VBA macros in Excel. The new VB Editor contains a lot of the features we are used to seeing in the Windows versions of Excel, or Excel 2011 for Mac. In the video above I highlight some of the many new improvements to the editor. Conceptual overviews, programming tasks, samples, and references to help you develop Excel solutions. Excel Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) reference Microsoft Docs Skip to main content.
Get certified
Mobile (learn on-the-go)
Microsoft Excel Vba Mac Userform
Regularly updated content

New to Excel or need a refresher? This online course is designed to give you a solid foundation in the basics of Excel for Mac.
Supports Excel for Mac 2016. Also available: Excel Basic (PC).
In 24 engaging lessons you will learn how to use math, statistical, logic and text functions, organize data by sorting and filtering, effectively present your data in several chart formats and more.
Whether you use Excel for work or study, these tutorials will start you on your journey to becoming an Excel Ninja! Learn more about how a GoSkills Excel certification can boost your career.
Video tutorials are recorded in Microsoft Excel for Mac 2016.
Want to be a more efficient Excel user? Start learning 200 of the best Excel shortcuts for PC and Mac.
Once enrolled, our friendly support team and tutors are here to help with any course related inquiries.
Auto- 720p
- 540p
- 360p
Certificate
Yes (learn more)
Accredited by
CPD
Video duration
2h 08m
The Ribbon
Microsoft Excel Vba Mac Pro
Identify the terminology and elements of the Ribbon.
The Work Surface
Recognize the main terms used to describe Excel’s work canvas.
Navigation
Utilize the keyboard or mouse to select cells and ranges in a spreadsheet.
First File
Create your first Excel file, enter data and create a table.
Formatting
Format cells by selecting fonts and color fills to make information more attractive.
Basic Math
Utilize basic mathematics including multiplication and division in Excel.
Formula Anatomy
Understanding Excel Formula Anatomy.
Cell Referencing
Learn about working with absolute and relative cell referencing, and techniques for copying formulas.
Function Anatomy
Use to understand the anatomy of Excel functions, and what their components mean.
Math Functions
Learn basic math functions including SUM, ROUND and SUBTOTAL.
Basic Statistics
Learn basic statistical functions including COUNT, COUNTA, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN, MEDIAN and MODE.
Logic Functions
Learn to build standalone logical IF functions, and make them more complex by nesting AND and OR within them.
Text Functions
Learn to break apart text with the LEFT, RIGHT, MID, FIND and SEARCH functions, and to combine text with the & character.
Conditional Math
Learn to use SUMIF, COUNTIF and SUMPRODUCT to add cells only when certain conditions are met.
External Links
Learn about creating and updating external links, and about the potential dangers of external links in Excel.
Sorting
Learn to sort data in Excel by a single column or by multiple columns.
Filtering
Learn to filter Excel data for specific words, dates, and apply multiple filters to a single data table.
Contiguous Data
Learn tricks for consolidating your data so it's vertically contiguous (without blank rows) – for Tables, PivotTables and Charts.
Cell Formatting
Learn to work with the Format Cells dialog to apply text rotation and borders, and to center data across multiple cells.
Building Column Charts
Learn how to create an effective column chart by reducing ink and 'noise' that distract from the main messages.
Building Bar Charts
How to create an effective bar chart by reducing ink and noise that distract from the story.
Building Pie Charts
Learn how to build an effective pie chart, and when you should and shouldn’t use them.
Building Line Charts
How to create an effective line chart through careful manipulation of chart elements to enhance its story telling ability.
Comments
Learn about creating, reviewing and printing Excel comments.
These days we all live and work in a multi-device, multi-platform world, and so when building Office 2016 for Mac, one of our key objectives was to make it as easy as possible to transition from using Office for Windows to using Office for Mac and back again. That’s why you’ll notice an interface that’s consistent with what you’d expect when using Office 2016 for Windows, and why we added support for virtually all of the Windows Excel Ctrl keyboard shortcuts. So when it came to working with external data, we applied that same logic: how can we make the experience great and working cross platform easier than ever?
External data in Excel 2016 for Mac
We examined how we could improve external data for Excel 2016 for Mac and made the following changes:
- Excel 2016 for Mac comes with a pre-installed and integrated SQL Server ODBC driver, which we worked hand-in-hand with Simba Technologies to provide.
- Excel 2016 for Mac has a brand new Microsoft Query (MSQuery) and Connection Manager to make creating and managing all of your data connections easier and more consistent with Windows.
Let’s take a deep dive into how each of these improvements can help you.
Native support for ODBC data connections
Excel 2016 for Mac supports ODBC data connections with SQL Server and Azure SQL Database right out of the box. This means several great things for anyone who works with external data:
- When creating or refreshing data connections to SQL Server, there are no third-party drivers required—everything you need is included right in the app.
- Connections made to SQL Server in Excel 2016 for Mac will work in Excel for Windows and vice versa. Have a workbook with ODBC data connections you’ve been using on Windows and never been able to use on your Mac? Well, now you can with cross-platform compatibility.
- If you want to connect to something other than SQL Server, we still have several great partners offering third-party drivers to connect to any data source you can imagine.
In addition, all of the ways in which you interact with external data are now consistent between the platforms. Looking for that Refresh button? It’s on the Data tab just as you’d expect.
The Data tab in Excel 2016 for Mac.
A better way to work with external data connections
Microsoft Excel Vba Programming
One of the biggest improvements to working with external data connections in Excel for Windows in recent releases has been the Connection Manager. It provides a central place to see all of the data connections in a workbook, see where they are used, and modify, remove or refresh each one individually. With Excel 2016 for Mac, you now have that same Connection Manager you are familiar with from Windows. All of your connections are displayed, and you can click any of them to see where they are used in your workbook and to perform any action.
The all-new Connection Manager in Excel 2016 for Mac.
The Connection Properties dialog has been streamlined as well to match Excel for Windows, so that you now only see the properties that apply to your particular data connection.
All of your connection properties are in one place and just like Excel for Windows.
However, what good is easier management of your data connections if it’s too hard to create them to begin with? With Excel 2016 for Mac, creating a connection to SQL Server is easier than ever. On the Data tab, simply select New Database Query > SQL Server ODBC, and you are presented with a simple connection dialog. Once it’s filled out, the newly redesigned MSQuery launches.
Microsoft Excel Vba Macro
The all-new MSQuery in Excel 2016 for Mac.
The new MSQuery experience is very similar to the SQL Query Analyzer that many of you have worked with. On the left is a listing of the databases and tables in your database that you can explore. At the top right is a color-coded SQL editor, and at the bottom right are the results of any query you run. Simply enter a SQL statement, click Run Query to make sure it works. Once it does, click Return Data to drop your data right back into your worksheet. And that’s it; your data is now in your Excel workbook, live and ready to use in Excel 2016 for Mac or Excel for Windows!
Working with a third-party data provider works the exact same way. The only difference is that after installing the data provider, you select New Database Query > From Database and then select your data provider from the Apple iODBC manager.
Microsoft Excel Vba Machine Learning
Now it’s your turn!
Excel Vba For Mac Tutorial
We think we’ve made huge strides in making external data easier than ever in Excel 2016 for Mac and we hope you do too. Give it a try and let us know of any questions or feedback you have in the comments!